Hello everyone, so in this blog, I will be talking about building neural networks from scratch. ps : this was my first talk.
Introduction
So, What are Neural Networks? These are a set of algorithms modeled loosely after the human brain usually designed to recognize patterns. They interpret sensory data through a kind of machine perception, labeling or clustering raw input. The patterns they recognize are numerical, contained in vectors, into which all real-world data, be it images, sound, text or time series, must be translated.
Fundamental Concepts You Should Know
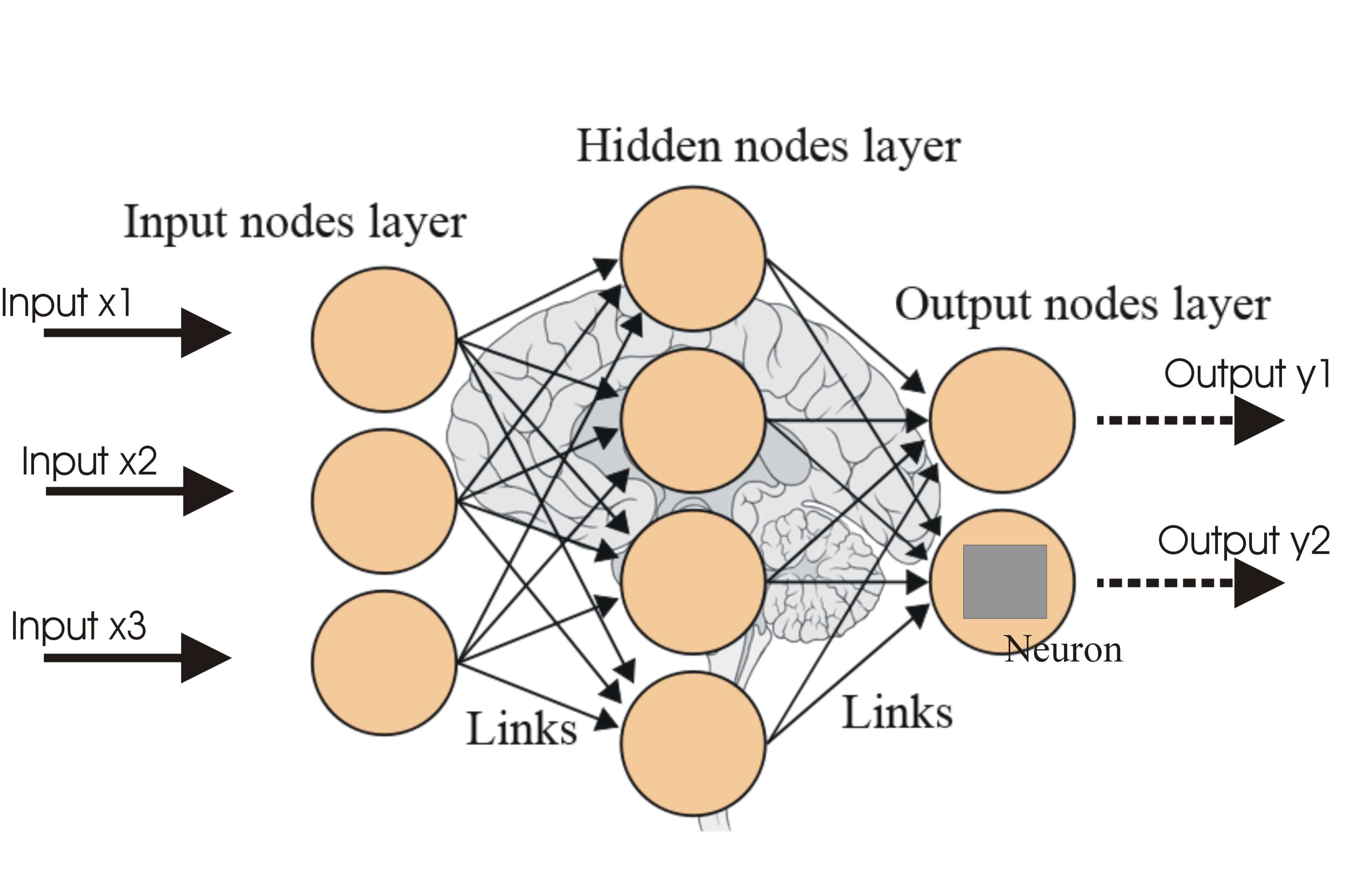
Before you begin building your own Neural Network, here are some key concepts that you should be having a good understanding of:
Layers: These are the building blocks of neural networks, with each layer transforming its input data to a more abstract level.Neurons: The fundamental processing units within layers that apply weights to their inputs and pass the result through an activation function.Weights and Biases: Parameters within neurons that are tuned during the training process to minimize the network’s error.Perceptron: This is the simplest type of an artificial neural network. It is a simple binary classifier that maps the input (which is a real-valued vector) to an output value (integer).Activation Function: This function decides whether a neuron should be activated or not. It takes a weighted sum of the inputs as an argument and returns a value between 0 and 1. There are multiple types of activation functions which could include ReLU, Sigmoid, tanH, etc.Loss Function: This measures the difference between the predicted and actual values. The goal of training is to minimize this function.Optimization Algorithm: This updates the parameters of the model in order to minimize the loss function.Backpropagation: This is the method used to update the weights of the network. It calculates the gradient of the loss function with respect to the weights and updates them accordingly.Optimizers: Algorithms that adjust the weights and biases to minimize the loss function.
What is Synthetic Spiral Data?
Synthetic spiral data is a set of two-dimensional data points arranged in concentric circles, with each circle representing a different class. Each point within a circle is assigned to that circle’s class. This type of data is often used in machine learning and data science tutorials because it’s relatively easy to generate and can illustrate complex concepts.
How to Build Your Own Neural Network?

Coming to the exciting part of this blog, hehe. You can follow this procedure to build your own neural network :
Designing the Network Architecture: Decide on the number of layers, neurons per layer, and activation functions.Initializing Parameters: Randomly initialize weights and biases.Forward Propagation: Compute the network’s output for a given input.Calculating Loss: Measure how far the network’s predictions are from the actual values.Backpropagation: Adjust the weights and biases in the direction that reduces loss.Iterating: Repeat the forward pass, loss calculation, and backpropagation for multiple epochs, using a dataset to train the network.
Code Examples
import numpy as np
class Layer_Dense: def __init__(self, n_inputs, n_neurons): self.weights = 0.10 * np.random.randn(n_inputs, n_neurons) self.biases = np.zeros((1, n_neurons))
def forward(self, inputs): self.output = np.dot(inputs, self.weights) + self.biases
class Activation_ReLU: def forward(self, inputs): self.output = np.maximum(0, inputs)
class Activation_SoftMax: def forward(self, inputs): exp_values = np.exp(inputs - np.max(inputs, axis=1, keepdims=True)) probabilities = exp_values / np.sum(exp_values, axis=1, keepdims=True) self.output = probabilities
class Loss_CategoricalCrossEntropy: def forward(self, y_pred, y_true): samples = len(y_pred) y_pred_clipped = np.clip(y_pred, 1e-7, 1 - 1e-7) if len(y_true.shape) == 1: correct_confidences = y_pred_clipped[range(samples), y_true] elif len(y_true.shape) == 2: correct_confidences = np.sum(y_pred_clipped * y_true, axis=1) neg_log_likelihoods = -np.log(correct_confidences) return neg_log_likelihoods
class Optimizer_SGD: def __init__(self, learning_rate=1.0): self.learning_rate = learning_rate
def update_params(self, layer): layer.weights += -self.learning_rate * layer.dweights layer.biases += -self.learning_rate * layer.dbiasesIn this code, we have defined several classes to represent different components of a neural network:
Layer_Dense: This class represents a fully connected layer of the neural network. It has a method forward for forward propagation.Activation_ReLU and Activation_SoftMax: These classes represent the activation functions used in the neural network. They have a method forward for forward propagation.Loss_CategoricalCrossEntropy: This class represents the loss function used to measure the difference between the predicted and actual outputs. It has a method forward for forward propagation.Optimizer_SGD: This class represents the optimizer used to update the weights and biases of the neural network. It has a method update_params for updating the parameters.
Techniques to Improve Accuracy
You could use the following strategies to improve the accuracy :
Increase the Number of Layers: More layers can lead to better feature extraction and improved accuracy.Increase the Number of Neurons: More neurons can provide a more complex and capable model.Increase the Number of Epochs: More epochs allow the model to learn from the data more thoroughly.Data Augmentation: Generating new training samples by applying transformations to existing data can improve generalization.Hyperparameter Tuning: Adjusting learning rate, batch size, and other parameters can lead to better performance.Regularization Techniques: Methods like dropout can prevent overfitting and improve model generalization.Transfer Learning: Using pre-trained models as a starting point can accelerate learning and lead to higher accuracy.
Conclusion

So, we’ve taken a deep dive into the fascinating world of neural networks figuring out how they work. Now, it’s your time to have some fun with it! Grab your coffee, get to biz and let your curiosity guide you as you explore and build. Enjoy the journey into Neural Networks!