Hello everyone, so in this blog, I will be talking about What, Why, How and Where's of MLOPs. Along with this, I would also be shedding light on two remarkable open-source stars of MLOps you should be using : MLFlow and ZenML.
Introduction
In the era of Machine Learning, operationalising models has become way more crucial than even training them. You dont want your models to be crashing into void and null especially when your clients would be using them.
MLOps is the hero here, which would help ensure that the development, versioning, deployment, monitoring, and constant improvements of these models happen seamlesslly together.
Think about this : Let’s say you build a model for fraud detection, you consider only a certain amount of parameters, yea?
NOW, the fraudster is smarter here. That person would be willing to use new tricks. Here, your model fails or if I may say, constantly degrades due to low performance. Here’s where you need to update your dataset, parameters, which leads to change in your machine learning model.
All of these processes can be done using : MLOPs
Components Involved in MLOPs
Model Development: This is a process of taking a trained machine learning model and integrating it into a production environment, making it accessible for making predictions or inferences on new, unseen data.Deployment: This refers to act of deploying various components of a ML system or an application to production environment.Monitoring: This is where you would essentially, keep a track on how the model is performing.Feedback Loops: As mentioned in the example above, here, you make continuous improvements based on user feedback.

MLFlow
MLFlow is a core platform in managing the ML lifecycle, offering tons of functionalities which are designed to simplify experimentation, tracking, packaging and deployment.
-
Role of MLFlow
-
Experiment Tracking: MLflow enables users to track and organize experiments by logging parameters, code versions, metrics, and output files. It also facilitates easy comparison of different runs, allowing data scientists to monitor and evaluate model performance across various hyperparameters and configurations. -
Model Packaging: It provides an interface to package models in different formats, which allows an easy deployment across platforms. MLflow also supports various deployment options, including batch inference, real-time serving through REST APIs, and integration with cloud platforms, simplifying the process of deploying models into production. -
Model Registry: This serves as a centralized repository for managing and versioning machine learning models. Helps track model lineage, and control versions. -
Model Monitoring and Management: It allows users to monitor deployed models’ performance over time by tracking metrics and comparing them against predefined thresholds.
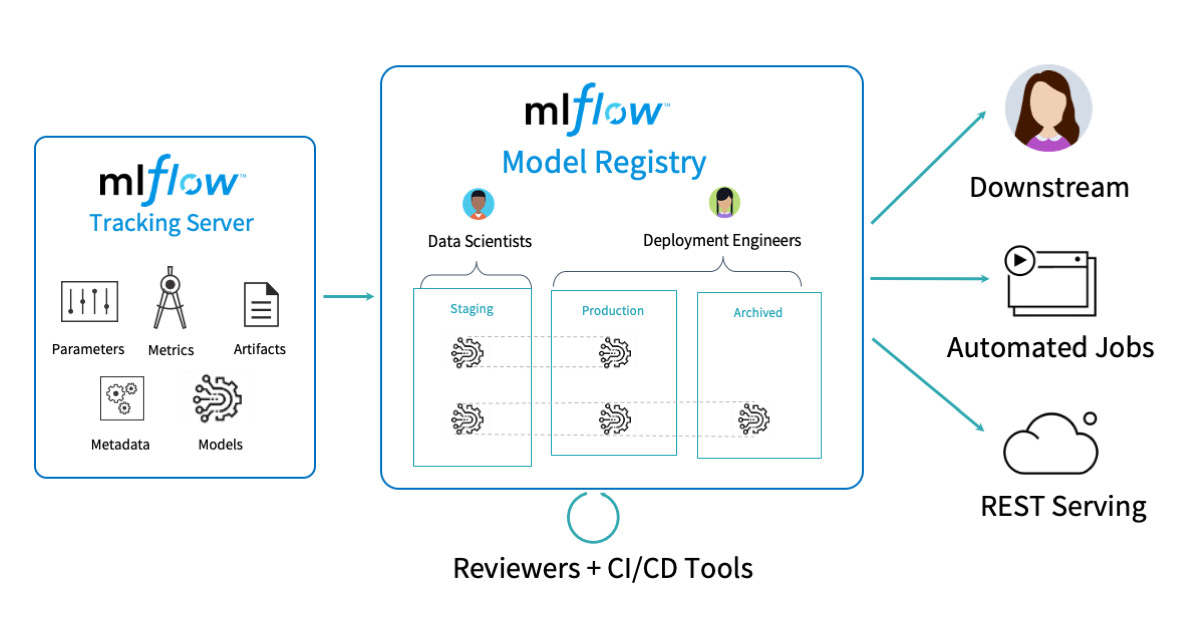
-
-
Simple Usecase
This code demonstrates how to use MLflow to manage experiments, log parameters and metrics, and save model artifacts, providing a comprehensive record of the machine learning workflow for better tracking, comparison, and reproducibility of experiments.import mlflowmlflow.set_experiment("experiment_name")with mlflow.start_run():# ----- ML Experiment goes here ----mlflow.log_param("param_name", param_value)mlflow.log_metric("metric_name", metric_value)# ----- Log model artifacts go here ----mlflow.log_artifacts("model_directory")
ZenML
ZenML is a robust pipeline orchestration tool, which emphasizes on data versioning, reproducibility and simplification of workflows. Due to these reasons, it facilitates a proper pipeline architecture, that again, helps you build reliable ML workflows.
-
Role of ZenML
Data Versioning and Organization: ZenML manages different versions of data efficiently, this in turn helps in easy tracking and access to specific data iterations. More so, that you have organised folder for different drafts of a document.Simplified Data Workflows: It simplifies complex data handling tasks by providing you an easy step by step methodology, this makes it easier for the data scientists to manage and understand the data pipeline.Collaboration and Control: Most importantly, ZenML acts like a collaborative platform where all the teams could work together, note the changes, control different versions of data pipelines which if put in an example : Think of it as a shared document where multiple people can edit simultaneously.Reproducibility and Monitoring: ZenML also ensures that when data or models are used by different team members or systems, they produce the same results consistently and accurately!

-
Simple Usecase
from zenml.core.steps import Evaluatorfrom zenml.core.repo import Repositoryrepo = Repository.get_instance()# Create a pipelinepipeline = repo.get_pipeline(name="my_pipeline")pipeline.add_evaluator(Evaluator(name="my_evaluator"))pipeline.run()This code sets up a basic ZenML pipeline by adding an evaluator step to assess a machine learning model’s performance within a project. It initializes, defines, and executes the pipeline within the ZenML framework.
Real-Life Applications
To not make things complex, lets take an easy example of prediction of customer churn in a telecommunication company. Customer churn btw is the number of paying customers who fail to become repeat customers.
Using MLFlow:
#This sample code is just to give you an idea.
#Using MLFLow Experiment here :
import pandas as pd from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split from sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score import mlflow
# Enable auto-logging to store run parameters, metrics, and metadata
mlflow.autolog()
data = pd.read_csv("whatever_dataset.csv")
''' Do all these processes : 1. Data Clearning 2. Data Transformation 3. Dimensionality Reduction 4. Train-Test Split 5. Handling Text/ Categorical Data ''' X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(features, target, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
mlflow.set_experiment("customer_churn_prediction") with mlflow.start_run(): rf = RandomForestClassifier(n_estimators=100, random_state=42) rf.fit(X_train, y_train) predictions = rf.predict(X_test) accuracy = accuracy_score(y_test, predictions)
mlflow.log_param("model_type", "RandomForestClassifier") mlflow.log_metric("accuracy", accuracy) mlflow.sklearn.log_model(rf, "RandomForestModel")This code shows the machine learning workflow using the RandomForestClassifier model, integrates MLflow for experiment tracking, logging parameters, metrics, and saving the trained model as an artifact for future reference or deployment.
Using ZenML :
from zenml.core.steps.evaluator import Evaluator from zenml.core.repo import Repository from zenml.datasources import CSVDatasource from zenml.pipelines import TrainingPipeline from zenml.steps.split import RandomSplit
repo = Respository.get_instance()
data_source = CSVDatasource(name = "Whatever you wanna name it", path = "whatever_dataset.csv")
training_pipeline = TrainingPipeline(name="CustomerChurnPrediction")
split = RandomSplit(split_map={"train": 0.8, "eval": 0.2})
evaluator = Evaluator()
training_pipeline.add_datasource(data_source) training_pipeline.add_split(split) training_pipeline.add_evaluator(evaluator) training_pipeline.run()This code sets up a machine learning pipeline using ZenML, specifying data ingestion from a CSV file, data splitting, and model evaluation steps, facilitating the workflow for building and evaluating a churn prediction model.
Conclusion
In conclusion, MLFlow and ZenML are really cool tools you could use when you’re hoping onto the field of MLOps. MLFlow is really good to use when you want to have real-time monitoring, model-packaging and experiment tracking. On other hand, ZenML is cool to be used for data versioning, workflow simplification, collaboration.
